Gel Electrophoresis: A Cornerstone Technique in Biotechnology
At Vetrona Biotechnology, we understand the critical role that precise and reliable laboratory techniques play in advancing scientific discovery. One such indispensable method is gel electrophoresis, a fundamental tool used to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins based on their size and charge. Whether you’re conducting research, performing genetic testing, or ensuring the quality of biotech products, gel electrophoresis is a technique that underpins countless applications in molecular biology, biochemistry, and beyond.
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
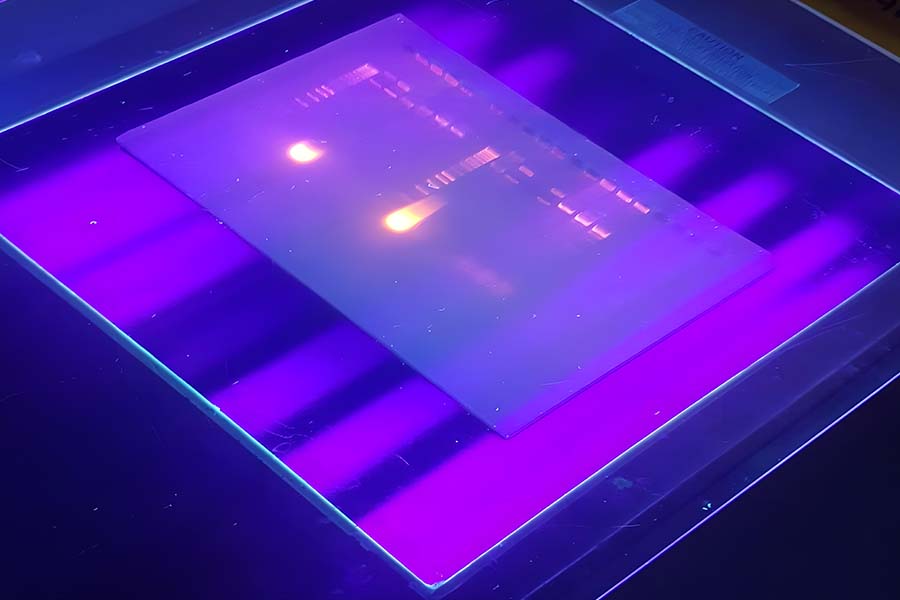
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory method that uses an electric field to move charged molecules through a gel matrix, allowing them to be separated by size. In the case of DNA and RNA, which are negatively charged due to their phosphate backbones, molecules migrate toward the positive electrode (anode) when an electric current is applied. Smaller fragments move faster through the gel’s porous structure, while larger fragments lag behind, resulting in distinct bands that can be visualized and analyzed.
For proteins, the process is similar but often requires additional steps, such as denaturing the proteins with detergents like SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) to give them a uniform charge, enabling separation primarily by size.
Types of Gels and Their Applications
The choice of gel matrix depends on the molecules being analyzed:
- Agarose gels are commonly used for separating DNA and RNA fragments. They are ideal for routine applications like verifying PCR products or analyzing restriction digests.
- Polyacrylamide gels (PAGE) are preferred for proteins and smaller nucleic acid fragments due to their finer resolution. SDS-PAGE, for example, is a standard method for separating proteins by molecular weight.
At Vetrona Biotechnology, we offer a range of high-quality pre-cast gels and gel preparation kits to suit your specific needs, ensuring consistency and ease of use in your experiments.
How Does Gel Electrophoresis Work?
The process of gel electrophoresis involves several key steps:
- Gel Preparation: A gel is prepared by dissolving agarose or polyacrylamide in a buffer solution and pouring it into a casting tray. Once solidified, wells are created to load the samples.
- Sample Loading: DNA, RNA, or protein samples are mixed with a loading dye and carefully pipetted into the wells.
- Electrophoresis: The gel is submerged in an electrophoresis chamber filled with buffer, and an electric current is applied. Molecules migrate through the gel based on their size and charge.
- Visualization: After the run, the gel is stained or exposed to UV light to reveal the separated bands. For DNA, fluorescent dyes like ethidium bromide or safer alternatives are used. Proteins can be visualized with stains like Coomassie Blue or silver staining.
Our state-of-the-art electrophoresis systems and imaging solutions at Vetrona Biotechnology make this process more efficient, allowing for precise control and high-resolution results.
Applications of Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a versatile technique with a wide range of applications:
- DNA Fingerprinting: Used in forensic science to identify individuals based on unique DNA patterns.
- Genetic Testing: Detects mutations or genetic variations by comparing DNA fragment sizes.
- Gene Expression Analysis: Analyzes RNA to study gene activity or protein profiles to understand cellular functions.
- Quality Control: In biotech manufacturing, gel electrophoresis verifies the size and purity of DNA fragments or proteins, ensuring product integrity.
At Vetrona Biotechnology, we leverage gel electrophoresis in our R&D and quality assurance processes to deliver reliable biotech solutions.
Advances in Gel Electrophoresis Technology
Recent innovations have made gel electrophoresis more efficient and user-friendly:
- Automated Systems: Multi-gel platforms allow simultaneous runs, increasing throughput.
- Digital Imaging: Advanced imaging systems provide accurate, real-time analysis and documentation of results.
- Safer Dyes: New fluorescent dyes offer high sensitivity without the hazards of traditional stains like ethidium bromide.
Vetrona Biotechnology stays at the forefront of these advancements, offering cutting-edge products that enhance lab productivity and safety.
Tips for Successful Gel Electrophoresis
To achieve optimal results, consider these best practices:
- Choose the Right Gel Percentage: Use lower percentages (e.g., 0.8% agarose) for larger DNA fragments and higher percentages (e.g., 2% agarose) for smaller fragments.
- Avoid Overloading: Too much sample can cause smearing or distorted bands.
- Monitor Voltage and Run Time: Higher voltages can speed up runs but may reduce resolution. Find a balance for your specific application.
Our technical support team at Vetrona Biotechnology is always available to provide guidance on optimizing your electrophoresis experiments.
Gel Electrophoresis in the Biotech Workflow
Gel electrophoresis is often a critical step in larger experimental workflows, such as:
- Preparing DNA for sequencing.
- Analyzing PCR products.
- Purifying specific DNA fragments for cloning.
By integrating seamlessly with other techniques, gel electrophoresis remains a cornerstone of biotech research and development.
At Vetrona Biotechnology, we are committed to supporting your scientific endeavors with high-quality products and expertise in gel electrophoresis. Whether you’re conducting routine analyses or pushing the boundaries of innovation, our solutions are designed to meet your needs.
For more information on our electrophoresis products and services, visit our website or contact our team today.